The Science Behind Climate Change Simplified
Climate change is not just a political or social issue—it’s a scientific reality backed by decades of data and research. Understanding the science behind it is essential for everyone.

The Greenhouse Effect
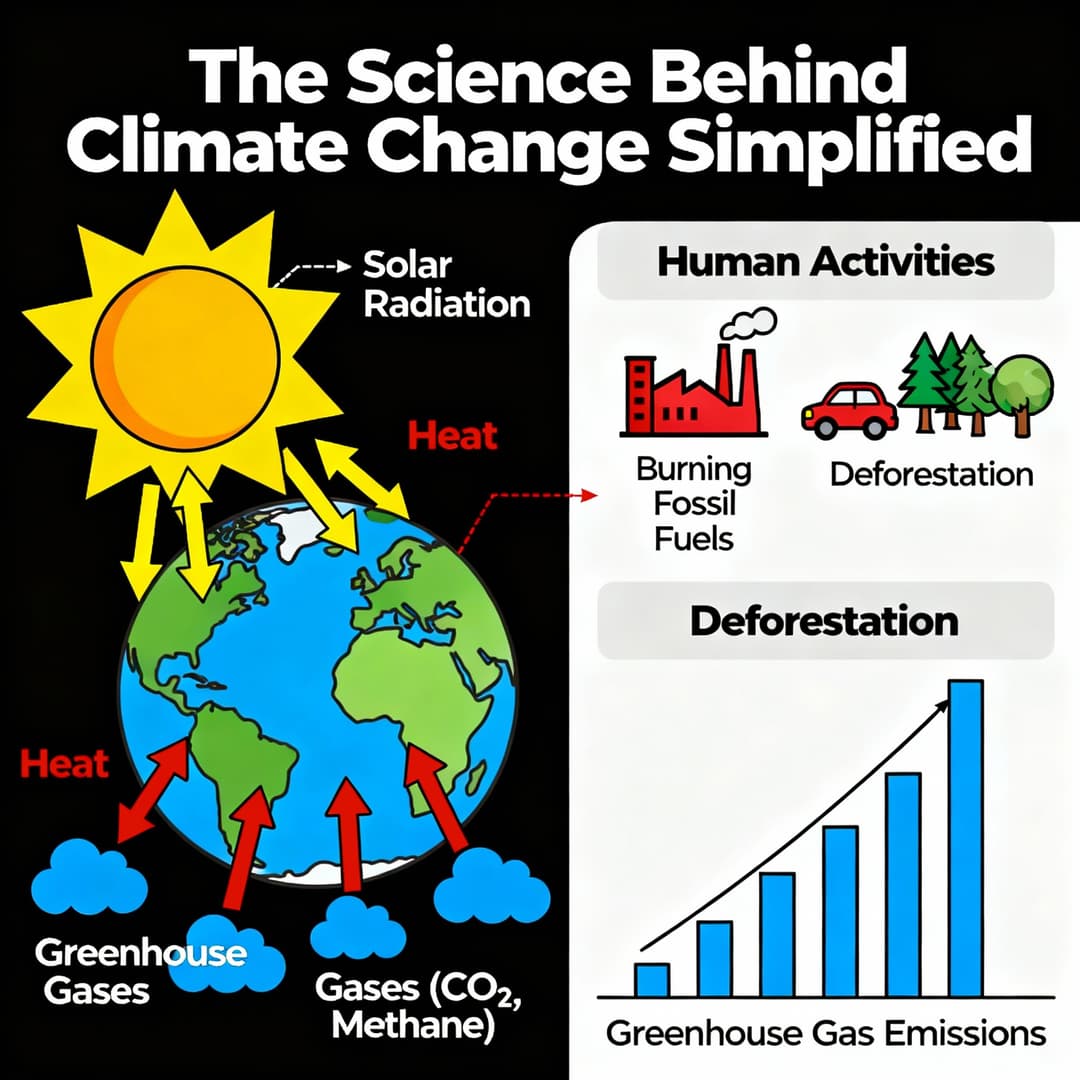
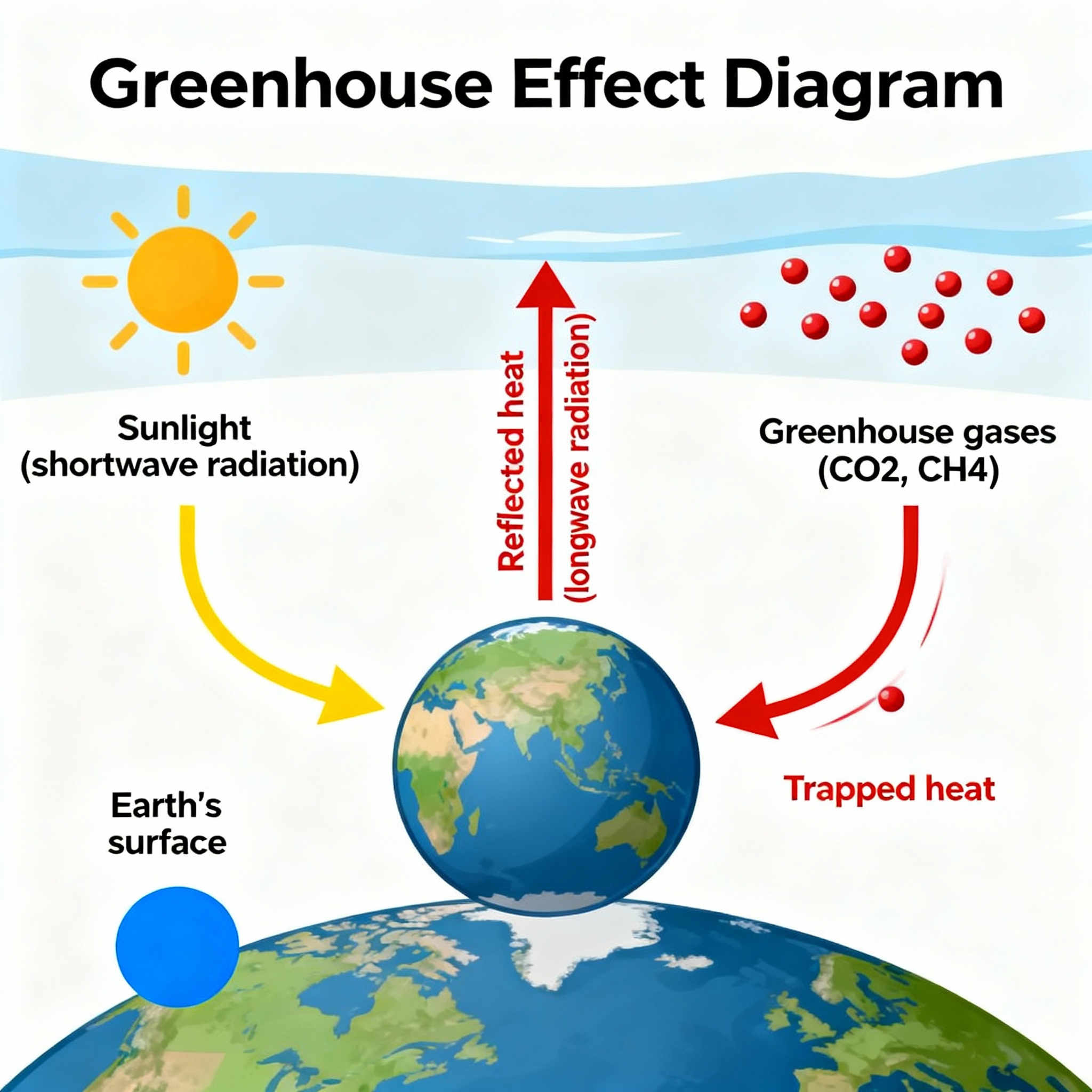
Earth’s atmosphere naturally traps heat from the Sun using greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), and nitrous oxide (N₂O). This keeps our planet warm enough to sustain life.
However, human activities—like burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes—have increased CO₂ concentrations, amplifying the greenhouse effect and causing global warming.
Key points:
- Greenhouse gases trap heat, maintaining Earth's temperature
- Human activities have increased CO₂ levels drastically
- Excess heat leads to melting ice, rising seas, and extreme weather
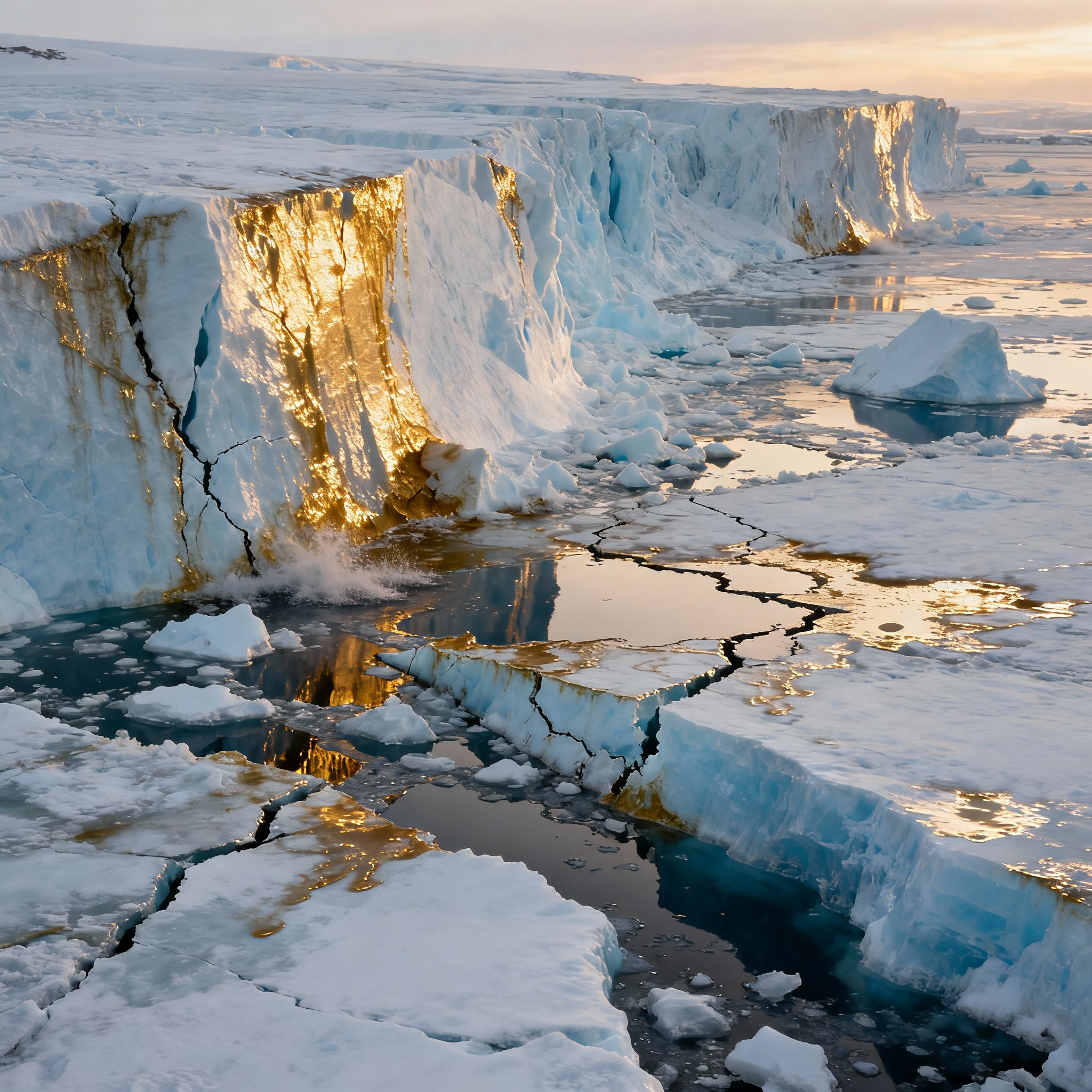
Observable Evidence
Global scientific agencies like NASA, NOAA, and the IPCC have documented changes over the last century:
- Average global temperatures are rising
- Arctic and Antarctic ice sheets are shrinking
- Sea levels are climbing steadily
- Extreme weather events—storms, droughts, floods—are more frequent and intense
These trends confirm that climate change is real and measurable.
Causes of Climate Change
- Fossil Fuel Combustion: Burning coal, oil, and natural gas releases large amounts of CO₂.
- Deforestation: Trees absorb CO₂, but cutting them down increases atmospheric carbon.
- Industrial Emissions: Factories emit greenhouse gases from manufacturing processes.
- Agriculture: Livestock and fertilizers release methane and nitrous oxide.

Solutions and Mitigation
Every individual and collective action can make a difference. Some effective solutions include:
- Renewable Energy: Solar, wind, and hydroelectric power reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Reforestation: Planting trees helps absorb CO₂ naturally.
- Cleaner Technologies: Electric vehicles, energy-efficient appliances, and sustainable farming.
- Global Policies: International agreements like the Paris Agreement aim to limit warming.
Small actions combined globally can help slow the pace of climate change and protect our planet for future generations.
FAQs
1. What is climate change?
Climate change refers to long-term alterations in temperature, precipitation, and weather patterns, primarily caused by human activity.
2. How do greenhouse gases work?
Greenhouse gases trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, keeping the planet warm enough for life. Excess gases amplify warming.
3. Can climate change be reversed?
While we can’t undo all changes, reducing emissions, planting trees, and adopting sustainable practices can slow or stabilize the effects.
4. Why are oceans important in climate change?
Oceans absorb much of the excess heat and CO₂, but this leads to rising sea levels, coral bleaching, and acidification.
5. How does climate change affect humans?
It increases the frequency of extreme weather events, threatens food and water security, and impacts health globally.
6. What can I do personally?
Use renewable energy, reduce waste, drive less, plant trees, and support eco-friendly policies and products.
7. Are renewable energies enough to stop global warming?
They are a crucial part, but combined efforts in reforestation, technology, policy, and individual actions are necessary.
8. How fast is climate change happening?
The last decade has been the hottest on record, indicating accelerated warming compared to historical trends.
9. Do all countries contribute equally?
No, industrialized nations historically contributed more CO₂, but emerging economies are increasing emissions too.
10. Why should we care about climate change now?
Immediate action is essential to prevent irreversible damage to ecosystems, economies, and human health.